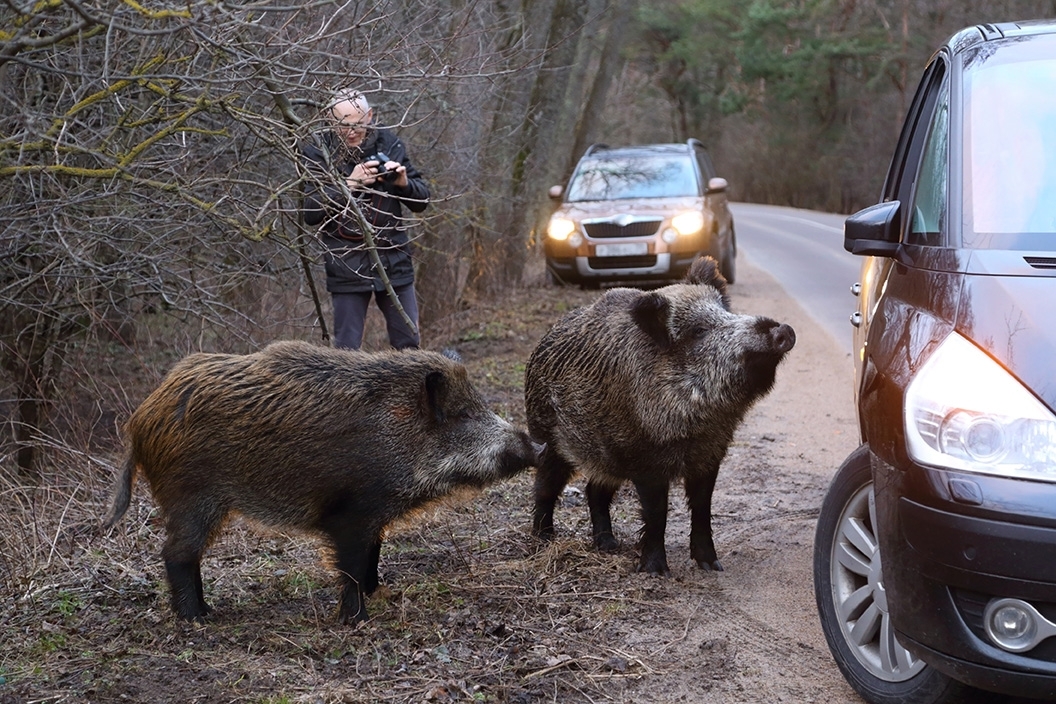
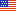
Feral swine cause tremendous damage to agriculture, including row crops, forestry, livestock, and pasture.
Damage to Agriculture
Crops
Feral swine damage crops by consuming them or by their rooting, trampling, and wallowing behaviors. Field crops commonly targeted by feral swine include sugar cane, corn, grain sorghum, soy beans, wheat, oats, peanuts, and rice; however, they will eat almost any crop. Farmers may also experience damage to vegetable and fruit crops such as lettuce, spinach, melons, and pumpkins.
Pasture
Feral swine damage pasture grasses, killing desired plant species and often encouraging the growth of undesired weed species. Feral swine will turn over sod and pasture, by rooting, to expose the tender roots of plants, grubs, and invertebrates which ultimately destroys the pasture. The ruts and rises this behavior creates can make it challenging, even impossible, for a farmer to drive a tractor over the field to harvest hay.
Livestock
Feral swine can transmit pathogens to livestock, which may result in financial losses to livestock producers due to lower productivity, veterinary costs, or even mortality. They are also capable of killing young calves and lambs, and vulnerable adult animals during the birthing process. Feral swine may also eat or contaminate livestock feed, mineral supplements, and/or water sources.
Horticulture
Feral swine can devastate orchards and vineyards by consuming fruit, berries, citrus, grapes, and nuts. Feral swine can destroy saplings and vines by roughly rubbing on the plants with their bodies (which they do to remove parasites from their skin) and can also damage large trees by scraping bark off with their tusks to mark territory, creating an entry point for diseases on the tree. Their rooting can severely damage, or even kill, saplings, shrubs and vines directly or by facilitating the spread of soil-based fungal diseases. Feral swine can also break irrigation lines, rip or tear nets, trellises, drying racks, and other specialized structures and equipment associated with orchards and vineyards.