Citrus Black Spot
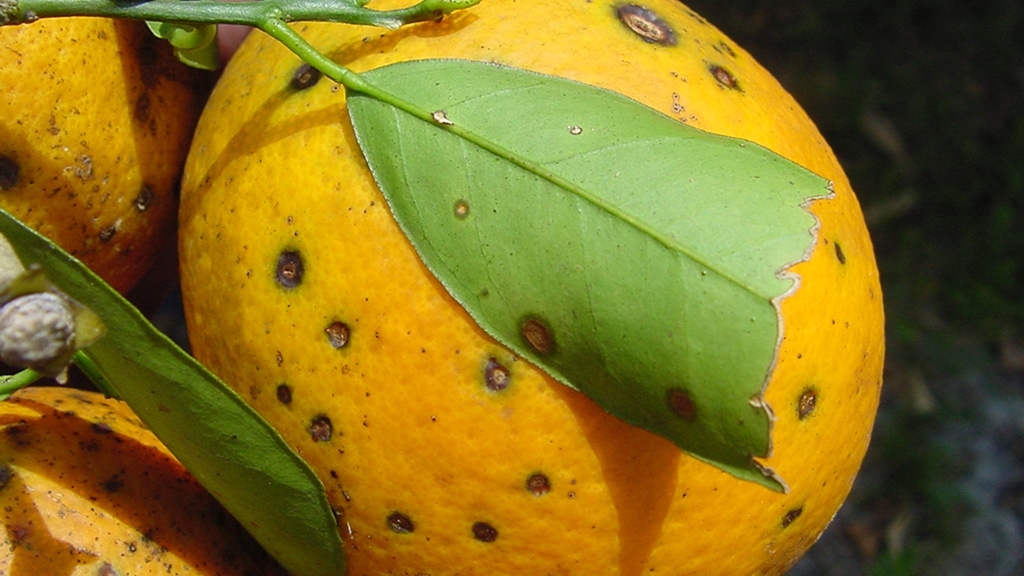

Citrus black spot is a fungal disease that leaves fruit speckled and lesioned but does not affect the internal quality of the infected fruit. Many citrus species are at risk for citrus black spot, making strict regulation and management necessary to prevent the spread of this disease.
Citrus black spot is caused by the fungus Phyllosticta citricarpa. It is spread through leaf litter, from fruit to fruit and leaves through rain splash, and through human-assisted movement.
When trees are severely infected, fruit may drop prematurely, resulting in significant yield loss. The disease was first identified in the United States in 2010 in Florida.
Symptoms can be found on fruit and leaves. They are are easiest to identify during "color break," when fruit turns from green to ripe coloration. Here's what to look for:
- Lesions on leaves
- Young lesions are small, round, slightly raised, reddish-brown with light centers and a diffuse yellow halo. Older lesions are sunken, with a gray center and dark brown margin.
- Lesions on fruit are diverse and grouped by symptom-based names.
- Hard spot lesions
- This is the most typical symptom of citrus black spot on fruits. They appear as the fruit matures, often around the time of color change. Look for as circular depressions that are 3 to 10 millimeters in diameter. Lesions have tan to gray centers with a distinct or prominent brick-red to dark brown margin. They develop on the side of the fruit most exposed to sunlight.
- False melanose
- Symptoms appear as numerous, small lesions that are dark brown, raised, and less than 1 millimeter (0.04 inch) in diameter. These lesions are much smaller than hard spot lesions. False melanose occurs on green fruit.
- Freckle spot
- These lesions are round depressions that are 1 to 3 millimeters (0.04-0.12 inches) in diameter and reddish in color. This type of symptom is considered a sign of a heavy infection. Freckle spot lesions can remain as single lesions or fuse into the virulent spot type of lesion late in the season or during storage.
- Cracked spot
- These lesions are dark, smooth, and variable in size with irregular margins and a cracked surface. They form on green fruit and remain visible on mature fruit. This symptom has only been observed in the Americas and is often found associated with rust mite damage.
- Virulent spot
- These lesions occur on heavily infected mature fruit toward the end of the growing season. They are discolored, sunken, and irregular lesions that cover a large area of the fruit. This symptom is caused by the expansion and/or fusion of other lesions. Virulent spot may accompany premature fruit drop and serious postharvest damage because the lesions may extend into the fleshy part of the fruit.
View images of citrus black spot.
- Know the quarantines in your area.
- Buy only USDA-certified citrus plants.
- Don't move branches, green waste, dead trees, and other regulated items out of a quarantined area.
- Don't mail or transport home-grown citrus fruit or plants out of a quarantined area.
- Commercial nurseries must follow strict protocols for moving citrus nursery stock (48.79 KB) out of quarantined areas.
Report Signs of Citrus Disease
If you think you’ve seen signs of this disease or pest, immediately report your findings to a State Plant Health Director.
Controlling Citrus Black Spot
At this moment, citrus black spot is only found in southern Florida.
- Conditions of Movement (Federal Orders)
- APHIS-Approved Packinghouse Procedures for Citrus Black Spot (172.98 KB)
- Protocol for Removing Areas from the Citrus Black Spot Quarantine (409.73 KB)
A potentially actionable suspect sample (PASS) is a regulatory sample1 from the environment or an APHIS-approved exclusionary facility2 where preliminary diagnostics indicate that Phyllosticta citricarpa, a USDA regulated pathogen, is present and must be confirmed by APHIS' Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL).
Samples Collected from a Non-Regulated Area
Any regulatory sample collected from a non-regulated area3 or APHIS-approved exclusionary facility that tests positive using APHIS-approved tests for the presence of Phyllosticta citricarpa, the causative agent for citrus black spot, is considered a PASS and must be forwarded to PPCDL for final determination. A sample4 should consist of symptomatic plant material (fruit or leaves).
Sample Diagnostics
USDA APHIS PPQ Science & Technology
Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory
9901 Powder Mill Rd. Bldg. 580
Laurel, MD 20708
Phone: (301) 313-9208 or (301) 313-9271
When forwarding materials, notify the lab by email (APHIS-PPQCPHSTBeltsvilleSampleDiagnostics@usda.gov). Include the number of samples, screening diagnostic results, and tracking information in this communication. Do not ship samples on Fridays or the day before a federal holiday.
Please see additional information for preparing and submitting samples.
Samples Collected from a Regulated Area
A regulatory sample collected in a regulated area5 where preliminary diagnostics indicate Phyllosticta citricarpa is considered a PASS and requires confirmation by PPCDL ONLY under the following conditions:
- The sample is an unusual detection (novel symptoms or new host), and/or
- The sample will result in the expansion of a previously established regulated area
If neither of these conditions apply, the sample should be evaluated by the State-designated laboratory for final determination.
Definitions
1 Regulatory Sample: This is a sample of regulatory concern to APHIS for citrus black spot collected by regulatory officials.
(Return to content)
2 APHIS-approved exclusionary facility: A greenhouse structure designed to exclude quarantine pests that is approved by APHIS to produce citrus nursey stock for interstate movement.
(Return to content)
3 Non-Regulated Area: Any area where citrus black spot is not known to occur in the United States.
(Return to content)
4 Sample: A sample refers to a fruit or single bag of leaves (5 to 12 symptomatic leaves). It is strongly encouraged that each sample (fruit or leaf) is from a single plant.
(Return to content)
5 Regulated Area: Any APHIS-recognized area where citrus black spot has been federally confirmed.
(Return to content)