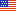
Mediterranean Fruit Fly

The Mediterranean fruit fly (Ceratitis capitata or Medfly) is considered the one of the most damaging agricultural pests in the world. It can infest a wide range of fruits, nuts, and vegetables, including apples, avocados, bell peppers, melons, and tomatoes. The damage makes crops inedible and unmarketable.
The Medfly has spread throughout the Mediterranean region, Southern Europe, the Middle East, Western Australia, South and Central America, and Hawaii. The first of numerous U.S. mainland infestations occurred in Florida in 1929.
- Appearance
- Medfly eggs are white, very small, and elongated.
- Larvae (maggots) are legless and white and feed inside the fruit.
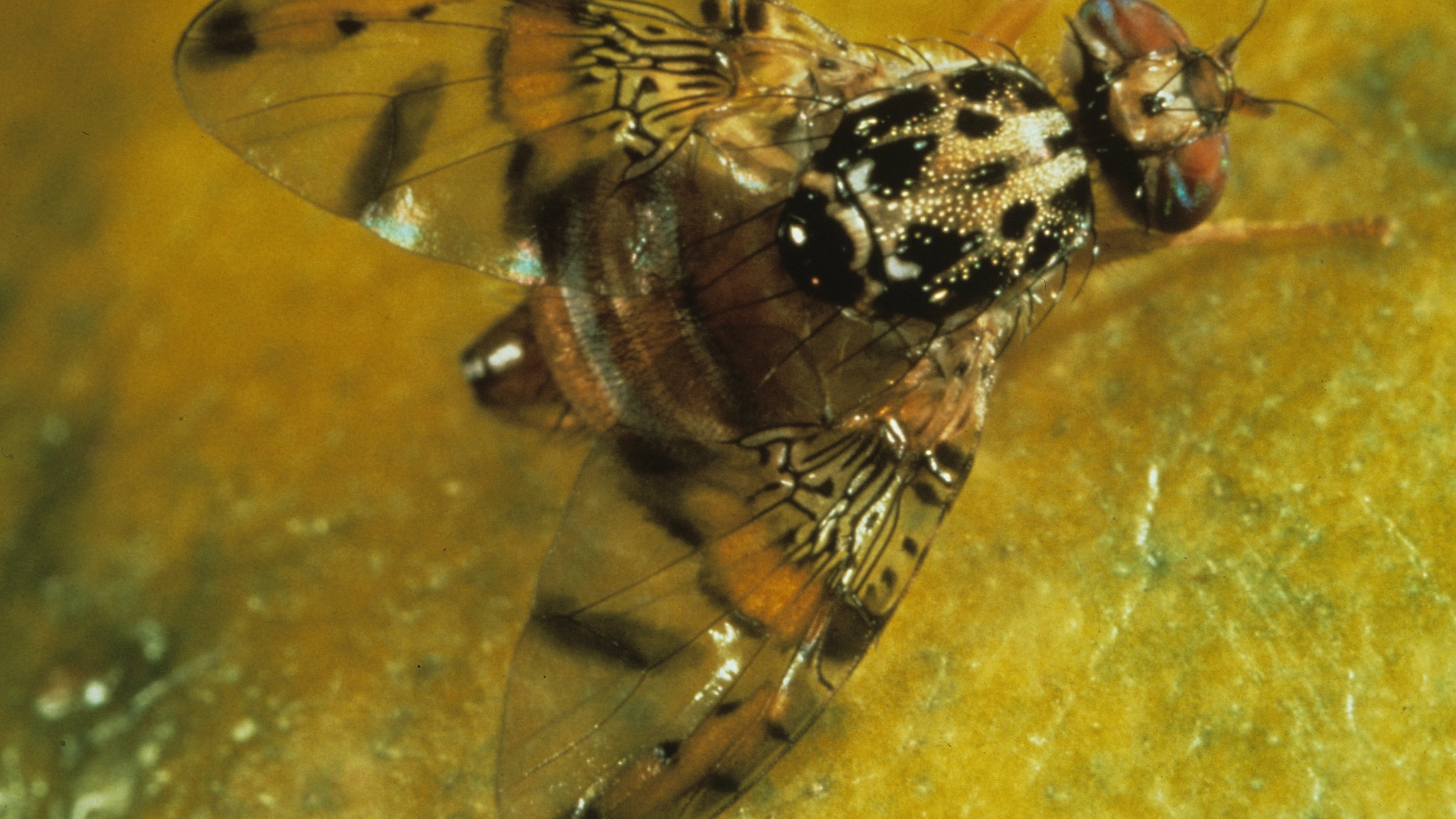
- Adult Medflies are smaller than a house fly. They have a blackish thorax marked with silver, a tan abdomen with darker stripes, and clear wings with light brown bands and gray flecks.
- Damage
- Fruit decays early and falls to the ground as the larvae develop and feed on the pulp.
The Medfly spreads mainly through infested fruits and vegetables. Here's what you can do to help prevent this:
- Fresh fruits, vegetables, or plants shouldn't be brought or mailed into your State or another State unless agricultural inspectors have cleared them first.
- When returning from international travel, declare all agricultural products to U.S. customs officials. Learn more on our Traveler Information page.
- Know and follow all quarantine restrictions in fruit fly-infested areas.
- Never remove fresh produce from your property if your area is under a fruit fly quarantine.
- Fruits and vegetables may be consumed or processed (juiced, frozen, cooked, or ground in the garbage disposal) at the property of origin. If not consumed or processed, double-bag fruits and vegetables in plastic bags before throwing them away.
- Cooperate with agriculture officials who may be in your area surveying for the pest. We may ask for access to your property to place and check insect-monitoring traps.
Report Plant Pests and Diseases
Have you seen this pest or signs of pest damage? Immediately report your findings to your State plant health director or State plant regulatory official.
If you suspect that you have a Medfly infestation, contact your local cooperative extension service for advice. Please cooperate with local, State, and Federal agricultural officials as they carry out their work.
Controlling Mediterranean Fruit Fly
In the United States, the Medfly is currently found in Hawaii.
California, Florida, and Texas are at high risk for Medfly.
For the latest Medfly quarantine information, select the name of your State in the Pest Tracker below, or view Fruit Fly Federal Orders and SPRO letters and Fruit Fly Maps and Descriptions.
Pest Tracker: Find Pests by State or Region
Find out if your State has a Federal quarantine and/or State-level quarantine for any hungry pests.
APHIS works with more than a dozen countries in the Greater Caribbean Region to conduct surveillance for Medfly and other exotic fruit flies. Our efforts help build regional surveillance capacity to maintain an early warning network for these damaging pests.
In the United States, we follow specific program guidelines (198.25 KB) to rapidly respond to a Medfly incursion. These guidelines address survey, treatment and regulatory response and meet the requirements of the National Environmental Policy Act and other applicable laws and regulations.
When we detect Medfly in an area, we work with State partners using a tiered approach. Our efforts may include surveying to delimit the extent of the incursion, conducting significant and ongoing public outreach, and establishing a parallel Federal-State quarantine in the affected area.
Our response may also include sterile insect technique (SIT) using aerial and ground dispersal. When we use SIT, we release large numbers of sterile male fruit flies to mate with female fruit flies in the wild. Because these females do not produce any offspring, the wild fruit fly population declines and is eliminated.
To support eradication and control programs, we release about 400 million sterile Medflies each month in Florida’s high-risk areas and about 200 million sterile Medflies in California’s Los Angeles Basin.